Intumescent Paint - How does it work?
A brief explanation on different types of intumescent coatings and how they and applied and perform during a fire.
United Spray
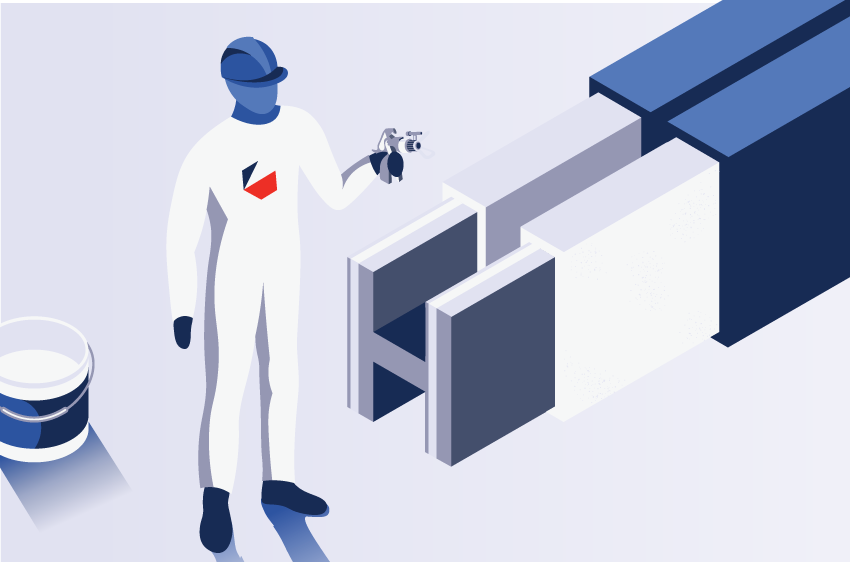
In a similar manner to SFRM material, intumescent paints are used as a coating for structural members and assemblies
(steel and concrete) to delay or prevent structural failure due to fire in a structure. However, unlike SFRM fireproofing,
these materials are widely used in structures where smooth and appealing finish is required (e.g., malls, train stations and
exposed steel members)
Intumescent paint comes mainly in two forms, thin and thick film. The thin film coating, is a water or solvent base
paint whereas the thick film coating is an epoxy-based material, and is used when higher protection is required, such
as marine off-shore structures, since it provides additional protection against corrosion.
These materials are applied in a similar manner to regular paint, through spray or rolling, however,
spraying is the most widely used application technique.
Intumescent Coating System
Intumescent coatings are always part of a system. Intumescent coating systems usually comprise several layers of different materials: a two-coat system (primer + intumescent) may be sufficient for low corrosive environments; a three-coat system (primer + intumescent + topcoat) may be preferred for more corrosive environments.
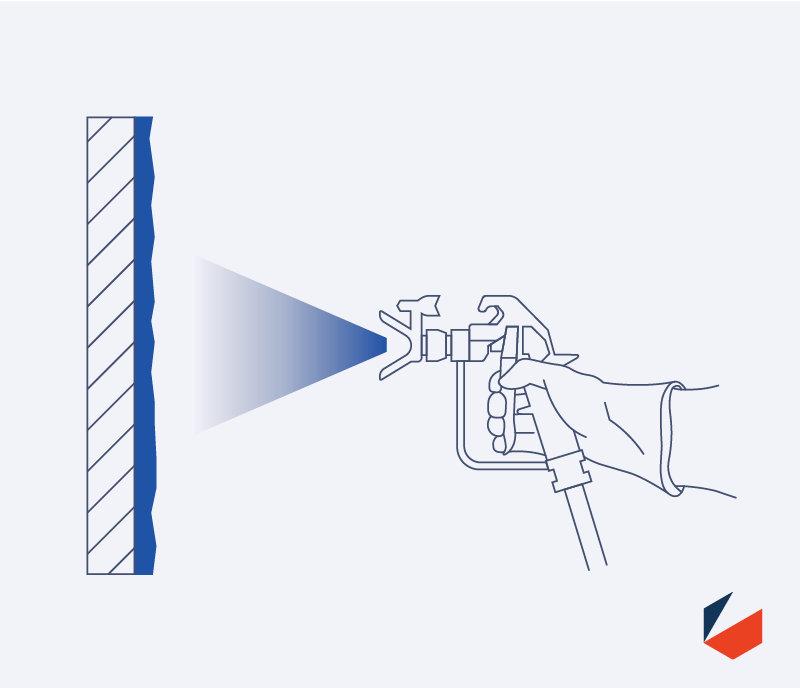
Surface preparation by application of primer
The primer is is first installed on the substrate to seal in any surface contaminants and provide a compatible surface for the Intumescent to in installed onto. Intumescent Coatings generally have a list of approved primers that are acceptable to use with the product.
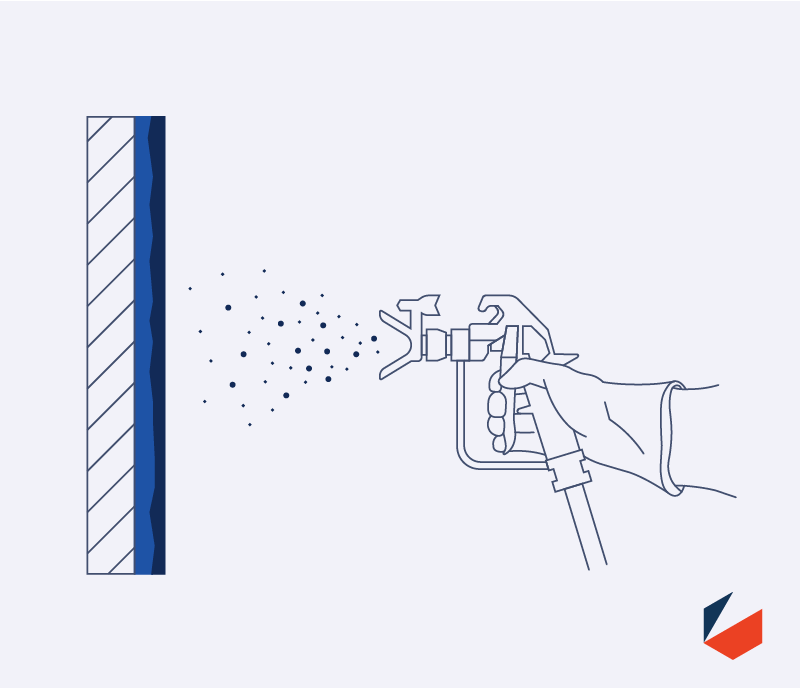
Intumescent application
Once the primer has been installed, the intumescent material is installed in multiple passes to achieve the specified thickness to provide the required fire rating. Thickness is measured is Mils (1 mil = 1/1000 of 1"). Water based this film materials can generally be applied 30-60 mils per pass with drying time in between each coat and epoxy materials can generally be install at 80-120 mils per pass.
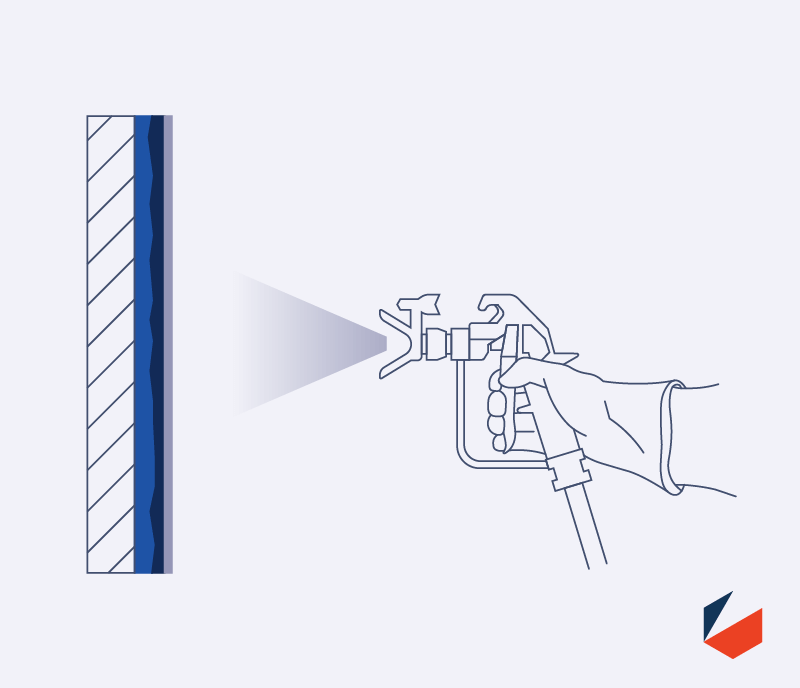
Topcoat application
Once the intumescent has been installed to the proper thickness the application of a topcoat is used to protect the underlying materials. Some topcoats can create a waterproof layer over water based intumescent to make them exterior grade, however an improperly installed topcoat can lead to future product failure.
How intumescent paints work?
Unlike other protective materials, during a fire, intumescent paint undergoes chemical reactions that allows it to expand, and form a char like foam layer with low thermal conductivity that protects the member from high temperatures.
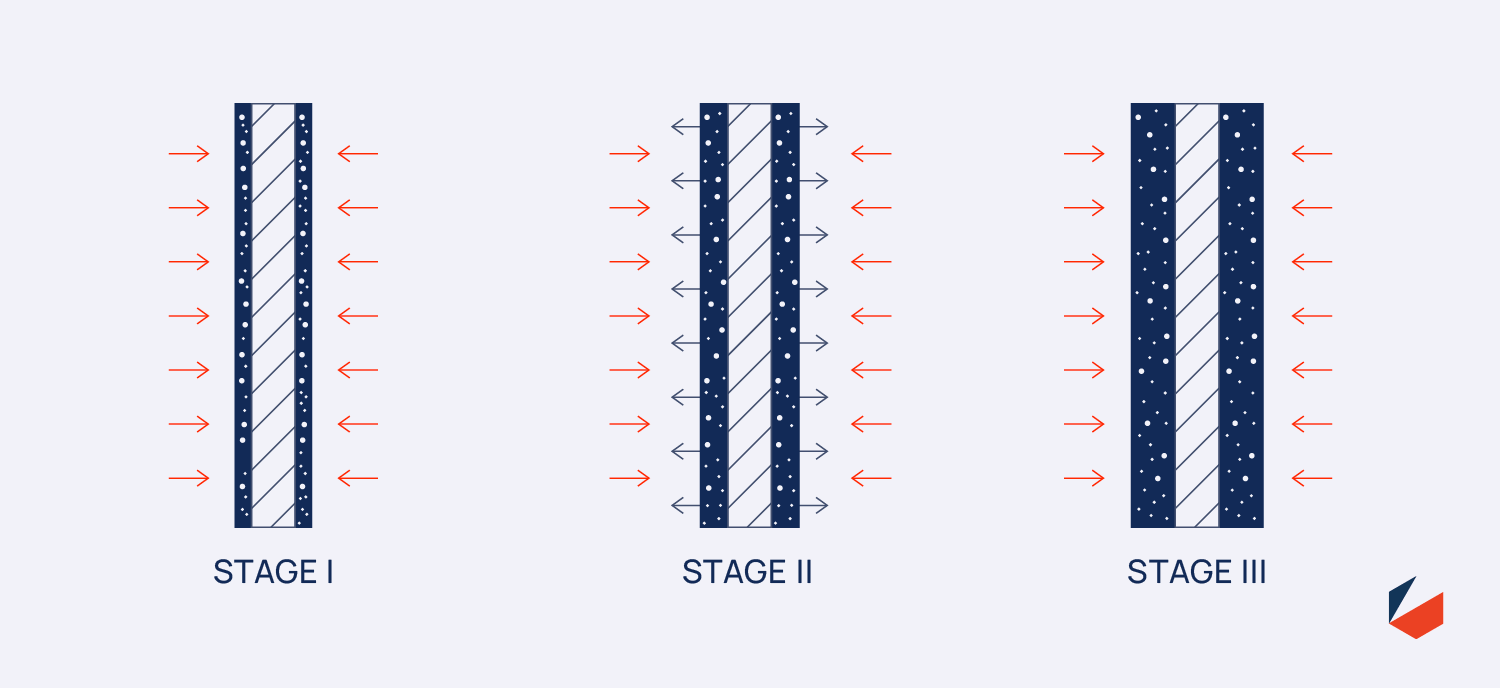
This protection process takes place in three stages.
The first stage takes place at temperatures below
or near 200 C – 250 C (392 F-482 F). During that phase, the intumescent paint, in its solid and original form, works as
insulator to protect the member. At higher temperatures, reaching up to 400 C (752 F), the base coat undergoes chemical
reactions, which releases inflammable gases such as carbon dioxide, ammonia and water vapor, leading to the expansion
of the coating up to 20 to 50 times the original volume, making the coating less dense and hence less thermally
conductive. At higher temperature, and during the final stage, the material in its expanded form acts as insulator and
transform into a solid char like foam that offers protection to the member for the required time period which could be up
to 4 hours.
As it is the case for other fire protection products, the applied intumescent coating should be in compliance with ASTM E119 and in accordance with UL 263 standards. In addition to that, similar to SFRMs, the thickness of application of the material is based on ratings provided by the UL Fire Directory, on the properties of the materials on hand and the shape and type of the member being protected. Even though intumescent paint is seen to have relatively higher costs than other alternatives, this fire protection system is characterized by high durability, its use on complex shapes and its ease of repair and maintenance, in addition to its smooth and aesthetic finish.
Do you want to learn why Intumescent Paint costs higher than alternatives?
Read our


